Checking for Signs of Diabetes
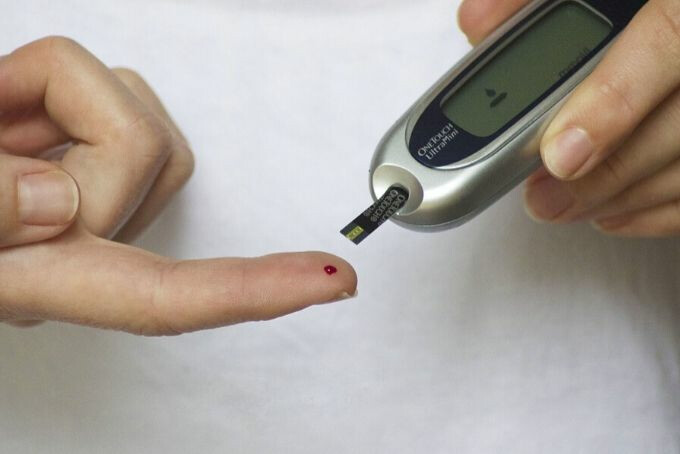
Diabetes is a disease in which blood sugar levels are chronically elevated. An estimated 10% of the US population is currently living with diabetes with that number expected to rise dramatically in the next few decades. The CDC estimates that as many as 1 in 3 Americans will be living with diabetes by mid-century. Diabetes is a dangerous disease as it affects not only quality of life, but greatly increases the risk for heart attacks, kidney failure, blindness and stroke.
November is National Diabetes Month and a perfect time to increase awareness for the prevention, symptoms and management of this disease:
- TYPE 1 DIABETES: 5% of diabetes is caused by insulin-deficiency. This is known as Type 1 diabetes (formerly known as juvenile diabetes). This autoimmune disease is triggered by the body’s own immune system attacking the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 1 is not preventable and must be treated with injections of insulin. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are extreme thirst, unexplained weight loss, frequent urination and fatigue. Type 1 commonly occurs in children and young adults, but may occasionally present in adults as well.
- TYPE 2 DIABETES: The majority of diabetics are living with type 2 diabetes which is characterized by insulin resistance. In this form of the disease, the pancreas produces enough insulin but the body is not able to effectively use it due to the cells resistance to the uptake of insulin. Genetics, as well as lifestyle play a significant role in the development of type 2 diabetes which is usually preventable. Steps to prevent and control type 2 diabetes are:
- Check your A1C: Know your numbers and have a fasting blood sugar done at least 1x per year; more often if you are at high risk.
- Physical activity: Aerobic exercise, resistance training and increased movement all contribute significantly to the body’s ability to respond to insulin.
- Lose weight through addition. Diets are usually only a temporary fix for weight loss, with most dieters adding the weight back on over time. An effective weight loss strategy focuses on adding in more high quality foods (vegetables, fruit, lean proteins, high-fiber carbohydrates, etc) and crowding out highly processed foods.
- Eat more plants: Plant based foods contribute to weight loss, blood sugar control and decreased inflammation. A diet high in plant based foods has been proven in prevention and even reversal of type 2 diabetes. Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas, etc.) are especially effective in managing weight and improving blood sugar control.
- Quit smoking. Smoking greatly increases risks for development of type 2 diabetes.
Exodus 23:25 You shall serve the Lord your God, and he will bless your bread and your water, and I will take sickness away from among you.
by Amy Beyer
Fitness Instructor & Nutrition Coach, Kelly’s Bootcamp



Login To Leave Comment